Creatine Unlocked: Fueling Cells and Elevating Cognitive Performance
Creatine supports energy balance in the body. It plays a key role in helping cells recycle adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP fuels countless processes in the body. Healthmasters Creatine (Pure pH-Buffered Creatine Capsules) provides 1,500 mg of creatine monohydrate in a three-capsule serving. The pH-buffered technology aims to stabilize creatine in acidic conditions. This technology protects the molecule as it moves through the digestive system. Once the creatine reaches cells, it can help maintain adequate energy levels.
This article explains the basic mechanisms of creatine. It also examines several clinical trials that investigated creatine’s impact on different cognitive and neuroprotective outcomes. These trials measured various markers of memory, structural plasticity, and mental performance. The results offer insights into creatine’s potential benefits for mental clarity, healthy aging, and overall cognitive function.
Mechanisms of Creatine: Why It Matters
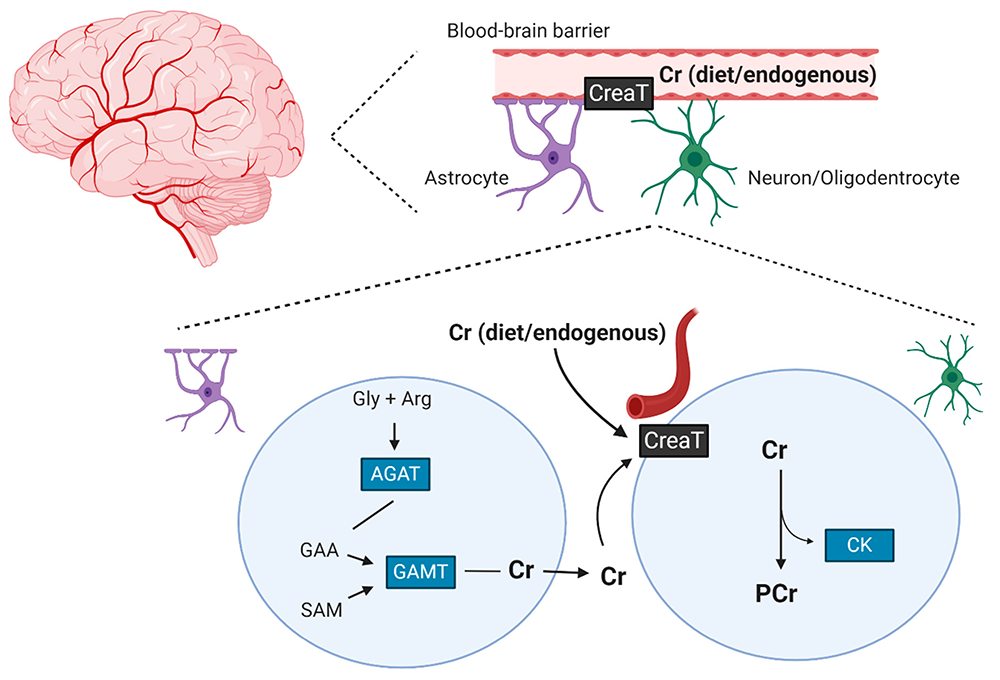
Creatine helps your cells produce and recycle energy. Cells use ATP as their main source of fuel. When ATP breaks down, it loses a phosphate group and forms adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Creatine, in its phosphorylated form called phosphocreatine (PCr), donates a phosphate group back to ADP. That process regenerates ATP. The name for this activity is the creatine kinase reaction. It keeps ATP supplies abundant during rapid energy demands.
Cells also defend themselves from oxidative stress. This kind of stress can disrupt normal cell operations. Researchers have linked this problem to impaired energy metabolism. Creatine may buffer cells against energy deficits. It can also support healthy mitochondrial function. In one study, researchers found that creatine helped maintain the shape and integrity of mitochondria [4]. Mitochondria generate most of the cell’s ATP, so stable mitochondria often improve energy status. Researchers have also noted that more creatine in cells could help maintain normal pH. That is why a pH-buffered creatine formula may increase this benefit.
Cognitive Performance Under Sleep Deprivation
Single-Dose Benefits
In a 2024 study published in Nature, researchers tested creatine on people during partial sleep deprivation [1]. The study focused on reaction time, memory scores, and attention span. Researchers noted that individuals who consumed a single, relatively large dose of creatine (.035 g/kg or about 160mg/lb) performed better on cognitive tasks. They also discovered higher levels of brain phosphocreatine. This suggested that creatine may support quick bursts of mental activity when energy levels dip. The scientists proposed that creatine helped compensate for the metabolic strain caused by lack of sleep. These findings highlighted creatine’s value during conditions that tax mental function.
Memory Enhancement and Reaction Time
Overall Cognitive Gains
In a 2024 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Nutrition, researchers examined studies of creatine’s impact on adult cognition [2]. They analyzed memory, mental speed, and concentration. Participants who consumed creatine showed small yet notable improvements in short-term recall tasks. They also showed slight gains in processing speed. The improvements varied by age and baseline diet. Some individuals who consumed low levels of dietary creatine appeared to see greater benefits. The meta-analysis underscored the link between enhanced phosphocreatine availability and sharpened cognitive function.
Recall and Learning in Healthy Individuals
In a 2022 systematic review and meta-analysis published in Nutrition Reviews, scientists reviewed data on healthy subjects [3]. They found that older adults saw stronger improvements than younger participants. Tasks involving word recall and figure recognition showed better results in those who supplemented with creatine. Investigators pointed to creatine’s role in securing extra energy in brain cells. This extra energy allowed more efficient communication among neurons, which helped sustain focus and memory accuracy.
Protective Effects in Neurodegenerative Contexts
Potential Support in Energy-Impaired Cells
A 2008 review in Neuromolecular Medicine focused on creatine’s therapeutic role for different neurodegenerative diseases [4]. Scientists discovered that unhealthy neurons often struggle to maintain normal energy turnover. For instance, some neurons show compromised mitochondria. Those mitochondria can fail to deliver enough ATP, leading to oxidative stress and cell damage. The review noted that creatine might strengthen cell membranes. It also might assist cells in resisting these damaging processes by stabilizing crucial energy pathways.
Brain Function and Health
A 2022 article in Nutrients emphasized the importance of creatine in maintaining brain energy levels [5]. Researchers summarized that creatine supplementation could raise phosphocreatine levels in specific brain areas linked to concentration and alertness. They also noted creatine’s potential to help individuals who face steady mental fatigue. This fatigue often appears in high-stress jobs or extended work sessions. Those tasks demand a consistent supply of energy in the brain.
Enhancing Hippocampal Plasticity and Cognitive Aging
Structural Changes Under Stress
In a 2025 study published in Food Science & Nutrition, scientists investigated creatine’s impact on structural plasticity in an aging mouse model [6]. They administered a chemical to prompt faster cognitive decline in mice. Those mice also received creatine supplements over time. The supplemented group retained better learning and memory skills. The hippocampus is central to new memory formation. Researchers found fewer signs of hippocampal synaptic damage in the creatine group. Creatine’s positive effect linked closely with higher activity of creatine kinase in the brain. Healthy creatine kinase activity indicates stable ATP production.
Protective Effects in a Huntington’s Model
In a 2000 study published in The Journal of Neuroscience, researchers tested creatine in mice genetically modified to resemble Huntington’s disease [7]. That disease often involves metabolic dysfunction. The mice taking creatine survived longer. They also showed less overall brain atrophy. Energy biomarkers remained closer to normal. Investigators explained that creatine likely stabilized the brain’s energy recycling system. This stabilization reduced the burden of constant metabolic stress. The results from this model have fueled discussions about creatine’s relevance in other disorders that involve energy deficits.
Insights for Alzheimer’s Disease
Possible New Therapy Direction
A 2023 article in Current Developments in Nutrition discussed creatine’s potential as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease [8]. The review noted that many individuals with Alzheimer’s disease have lower levels of brain creatine. Some also have deficits in mitochondrial function. Researchers suggested that creatine supplementation could help those neurons better manage their energy needs. This proposed mechanism might delay cognitive decline in certain cases. They called for further clinical trials in people with Alzheimer’s disease to test this hypothesis. While many factors shape Alzheimer’s outcomes, scientists remain hopeful that creatine can contribute to better energy regulation in vulnerable neurons.
Conclusion
Healthmasters Creatine (Pure pH-Buffered Creatine Capsules) delivers a stable form of creatine monohydrate. It offers 1,500 mg of creatine in three capsules. The specialized pH-buffering technology aims to protect creatine molecules from damage in the stomach. Once in the body, creatine supports efficient ATP recycling. This supports energy availability for muscle tissue and the nervous system. The studies summarized here highlight creatine’s role in short-term mental performance, ongoing cognitive tasks, and resilience under stress. They also point to creatine’s potential as a neuroprotectant in older adults or individuals with energy-compromised cells.
Individuals wanting to promote a healthy mind and body may add creatine to their daily routine. Research points toward creatine’s ability to enhance or maintain healthy cognitive performance. Many studies have shown improvements in areas ranging from sleep-deprived mental tasks to longer-term neuron health. Although more large-scale human trials will deepen our understanding, current evidence supports creatine as a versatile supplement for overall wellness. Healthmasters Creatine (Pure pH-Buffered Creatine Capsules) helps deliver a premium form of creatine, supporting cells secure the energy they need for daily function and healthy aging.
References
[1] Single dose creatine improves cognitive performance and induces changes in cerebral high energy phosphates during sleep deprivation (2024). Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-54249-9
[2] The effects of creatine supplementation on cognitive function in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis (2024). Frontiers in Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2024.1424972
[3] Effects of creatine supplementation on memory in healthy individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (2022). Nutrition Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuac064
[4] Creatine and Its Potential Therapeutic Value for Targeting Cellular Energy Impairment in Neurodegenerative Diseases (2008). Neuromolecular Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-008-8053-y
[5] Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Brain Function and Health (2022). Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14050921
[6] Long-Term Creatine Supplementation Improves Cognitive and Hippocampal Structural Plasticity Impairments in a D-Gal-Induced Aging Model via Increasing CK-BB Activity in the Brain (2025). Food Science & Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.4767
[7] Neuroprotective Effects of Creatine in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Huntington's Disease (2000). The Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.20-12-04389.2000
[8] Creatine as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease (2023). Current Developments in Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.102011
*The matters discussed in this article are for informational purposes only and not medical advice. Please consult your healthcare practitioner on the matters discussed herein.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Healthmasters' products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.


